- Hits: 3411
XRAMS Mechanical Design
Electrons accelerator design :
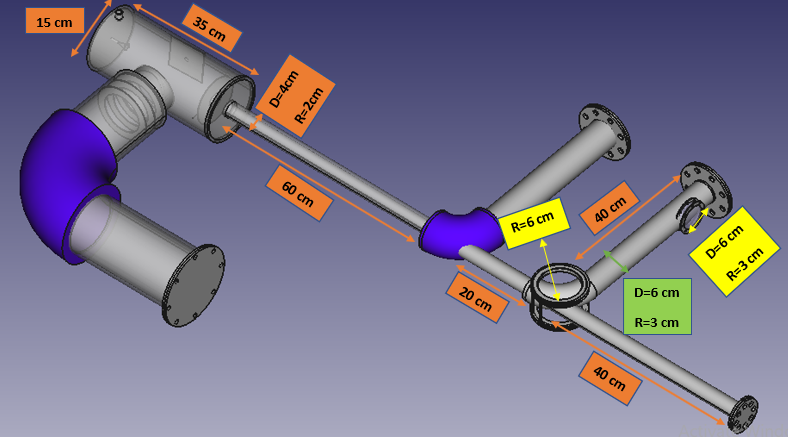
Mechanical design of eletrons accelerator (FreeCad)
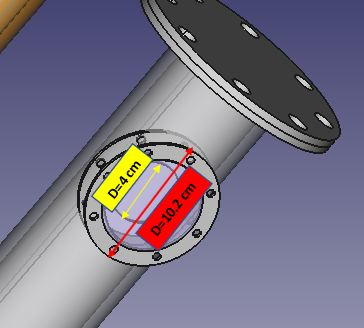
X-Ray glass thickness : 8 mm
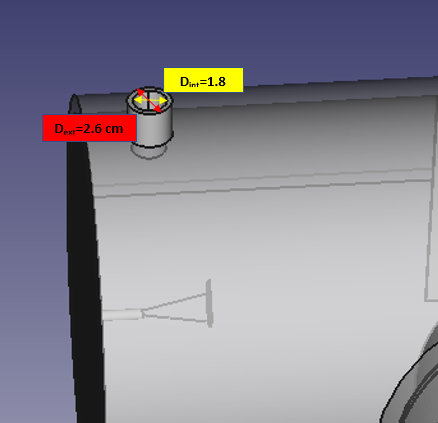
Place of entry of the gas sample :
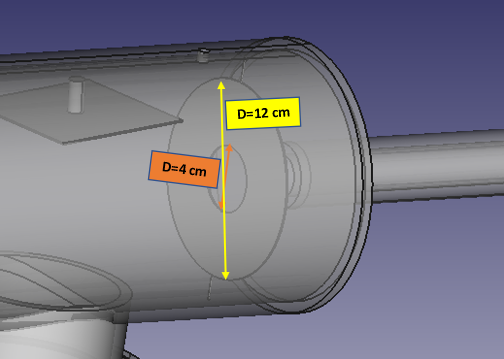
the anode :
Lead Box :
Lead box for safety from X-rays (FreeCad)
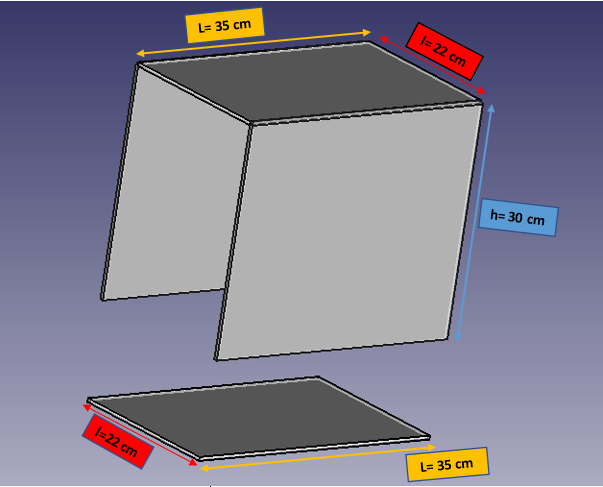
thickness of lead sheet: 1 mm

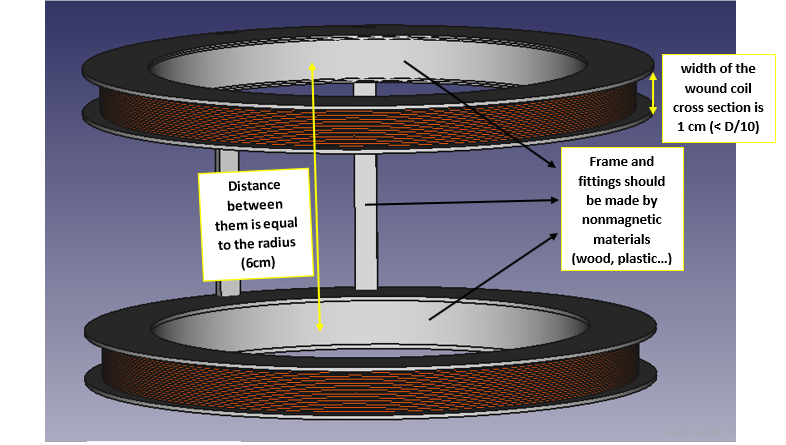
Helmholtz Coil design :
Mechanical design of Helmholtz coil (FreeCad)
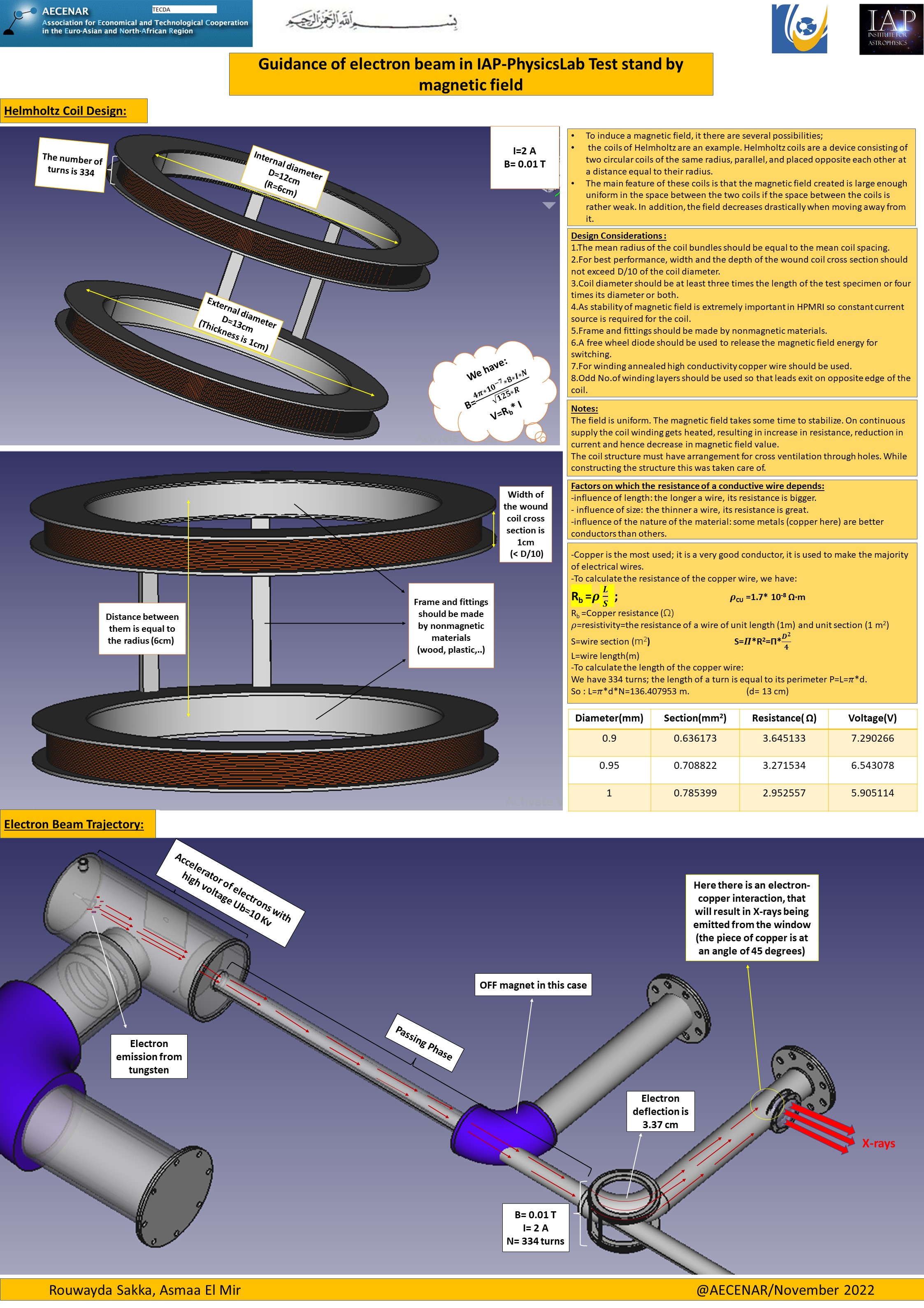
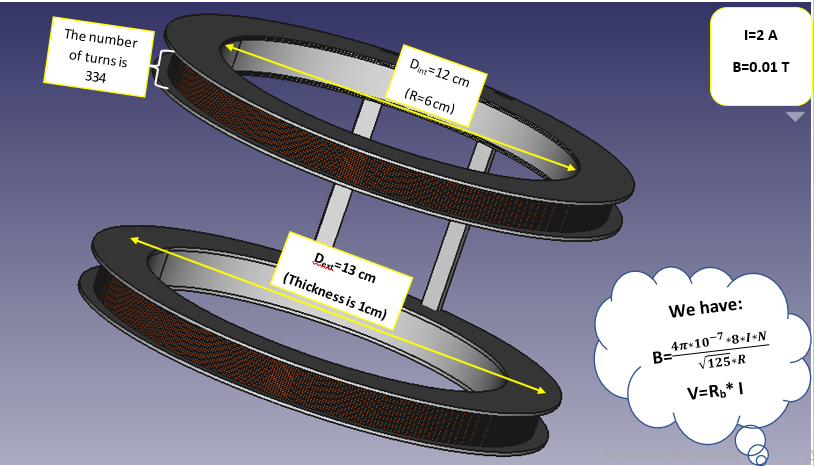
Concept
X-rays are created by bombarding a tungsten target with electrons inside a device known as the x-ray tube. To generate this stream of electrons inside the x-ray tube, a powerful x-ray generator first takes the regular alternating current (AC) electricity from the power line at about 120 to 480 volts and transforms it into power in the range of 35 to 150 kilovolts (kV or thousands of volts). When this very high voltage potential is applied to the x-ray tube, a tight beam of electrons is fired out of a small wire (called the cathode) and strikes a metal disk (called the anode). When this stream of electrons hits the special metal compound of the anode (often tungsten or alloys including tungsten), it causes x-ray energy to be released from the metal's atomic structure.
X-Ray detector amplifier
charge amplifier
for more information please download the full report:
Related Sites/Items
|
System Specification |
|
|
Mechanical Design |
|
|
Process Control System Spec./Design |
|
|
Mechanical Realization |
|
|
Process Control System Realization (PLC+GUI) |
|
|
System Test Specification |
|
|
System Testing |
