- Hits: 2611
system concept / system design
Raw materials for biogas production
Although, cattle dung has been recognized as the chief raw material for bio-gas plants, other materials like night-soil, poultry litter and agricultural wastes can also be used.
Advantages of biogas production
- It is a eco-friendly fuel.
- The required raw materials for biogas production are available abundantly in villages.
- It not only produces biogas, but also gives us nutrient rich slurry that can be used for crop production.
- It prevents the health hazards of smoke in poorly ventilated rural households that use dung cake and fire-wood for cooking.
- It helps to keep the environment clean, as there would be no open heap of dung or other waste materials that attract flies, insects and infections
- Availability of biogas would reduce the use of firewood and hence trees could be saved.
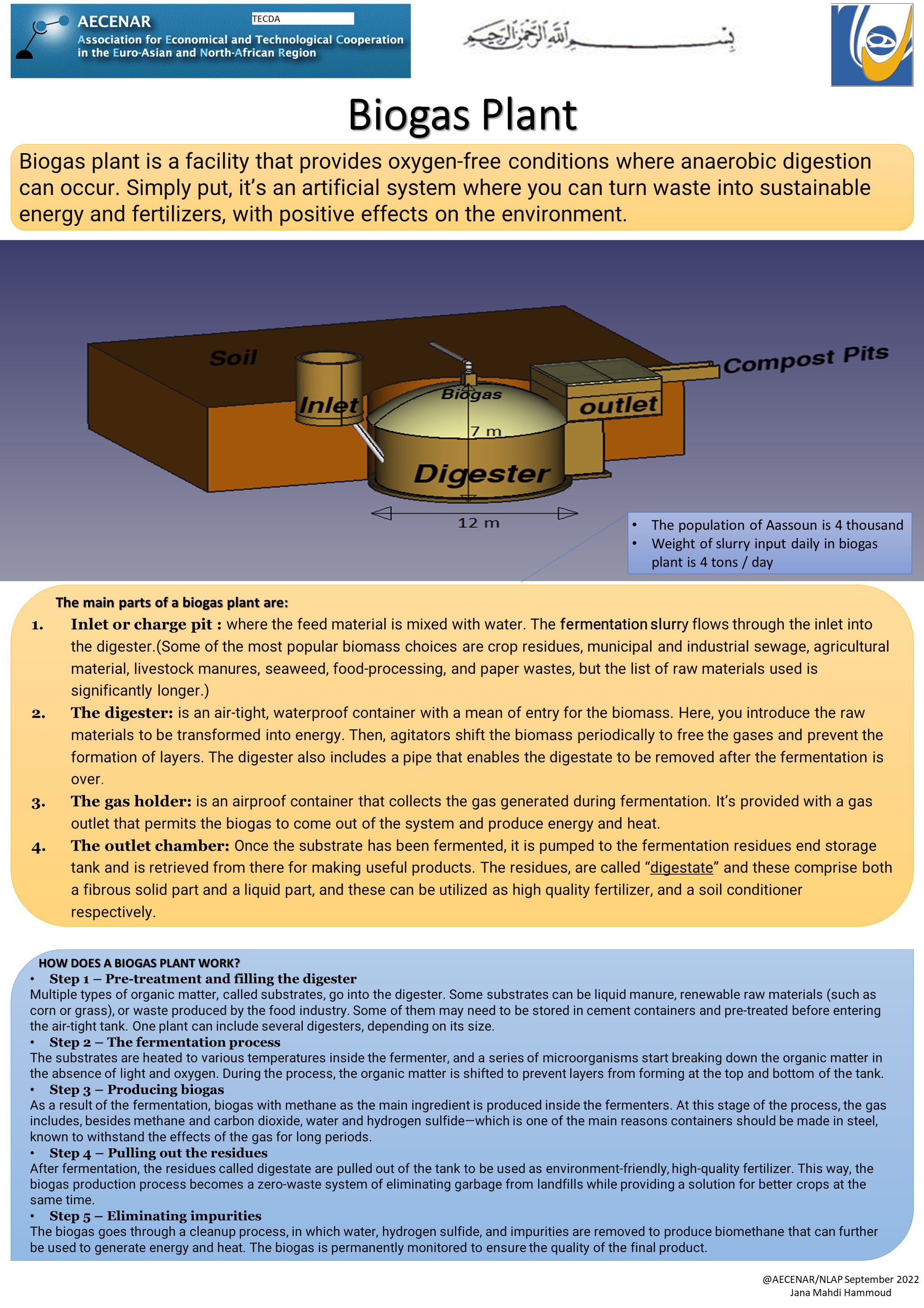
Components of biogas plants
- Mixing tank - The feed material (dung) is collected in the mixing tank. Sufficient water is added and the material is thoroughly mixed till a homogeneous slurry is formed.
- Inlet pipe - The substrate is discharged into the digester through the inlet pipe/tank.
- Digester - The slurry is fermented inside the digester and biogas is produced through bacterial action.
- Gas holder or gas storage dome - The biogas gets collected in the gas holder, which holds the gas until the time of consumption.
- Outlet pipe - The digested slurry is discharged into the outlet tank either through the outlet pipe or the opening provided in the digester.
- Gas pipeline - The gas pipeline carries the gas to the point of utilization, such as a stove or lamp.
Points to be considered for construction of a biogas plant
Site selection
While selecting a site for a biogas plant, following aspects should be considered
- The land should be levelled and at a higher elevation than the surroundings to avoid water stagnation
- Soil should not be too loose and should have a bearing strength of 2 kg/cm2
- It should be nearer to the intended place of gas use (eg. home or farm).
- It should also be nearer to the cattle shed/ stable for easy handling of raw materials.
- The water table should not be very high.
- Adequate supply of water should be there at the plant site. The plant should get clear sunshine during most part of the day.
- The plant site should be well ventilated.
- A minimum distance of 1.5m should be kept between the plant and any wall or foundation.
- It should be away from any tree to prevent root interference.
- It should be at least 15m away from any well used for drinking water purpose.
Availability of raw materials
The size of the biogas plant is to be decided based on availability of raw material.
Optimum conditions for anaerobic fertilizer synthesis:
- Temperature which depends on microorganisms, so that we have:
- Ambient (temperature < 25̊ C) and this is the temperature that we are going to work within.
- there are also mesophilic microorganisms that are active at a temperature range between 25º C and 45̊
- and thermophilic microorganisms that are active at a temperature > 45º C
- PH range should be between 6.6 and 7.8.
The optimum PH = 6.8.
https://www.flandershealth.us/anaerobic-digesters/alkalinity-and-ph.html
- And the ratio C/N = 25:1.
Here is the initial C/N ratio of various raw material from previous published studies:
Formula 1: C/N Ratio of Raw Materials = %C/%N
A Bokashi composting system uses anaerobic bacteria (lactic acid bacteria) and yeasts to break them down. This works well for both home and commercial kitchens.
C/N ratio of bokashi:
A1, A2, An: individual raw material
Fertilizers condition:
- Soil pH affects the amount of nutrients and chemicals that are soluble in soil water, and therefore the amount of nutrients available to plants. Some nutrients are more available under acid conditions while others are more available under alkaline conditions. However, most mineral nutrients are readily available to plants when soil pH is near neutral.
Soils can be classified according to their pH value:
- 6.5 to 7.5—neutral
- over 7.5—alkaline
- less than 6.5—acidic, and soils with pH less than 5.5 are considered strongly acidic.
-
species
C/N ratio
Trees leaves
Alder
15:1
Ash
21:1
Elm
28:1
Black older
22:1
Hain beam
23:1
Linden
37:1
Maple
52:1
Oak
47:1
Olive leaves
14,7:1
Leaves C/N ratio range
35-70
Leaves C/N ratio mean
50-54
fruits
Orange
100:10
Banana
35:1
apples
35:1
Fruits waste
35:1
Vegetable wastes
Cabbage ((ملفوف
12
Lettuce خس))
3.7
Potato peel
17.1
Potato and chips
48:1
Vegetable waste C/N range
10-17
Vegetable waste C/N mean
14
beans
Chick pea (حمص)
33
Lentil(عدس)
29
Wheat (قمح)
80:1
rice bran (نخالة الذرة)
23,48
corn
53:1
Corn skin
15
Dry pea
18
Meals ground from bean or seeds a C/N ratio
7:1
Coffee ground
20
Chicken
56:1
Chicken bone
5:1
bread
50:1
Rice straw
60:1
paper
173:1000
